I. Basics of Standard Transparent PC Plastic
- Chemical Definition
- Chinese Name: 聚碳酸酯 (Polycarbonate, PC)
- Molecular Structure: A high polymer containing carbonate groups (-O-C(=O)-O-), classified into aliphatic, aromatic, and hybrid types.
- Industrial Applications: Only aromatic polycarbonate achieves large-scale production due to its superior mechanical properties, ranking as the fastest-growing material among the top five engineering plastics.
- Synthesis Process
- Raw Materials: Bisphenol A + phosgene (phosgene method) or diphenyl carbonate (melt transesterification method).
- Key Properties:
- High light transmittance (amorphous glass state).
- Impact resistance (Izod notched impact strength: 600-900 J/m).
- Heat resistance (heat deflection temperature: ~137°C).
- Advantages & Limitations
- Strengths: High toughness, flame retardancy (UL94 V-2), electrical insulation, and ease of processing.
- Weaknesses: Poor hydrolysis resistance, notch sensitivity, UV-induced yellowing, and moderate wear resistance.
II. FLIERMOUSE Near-Infrared (NIR) Transmissive PC Plastic

- Core Features
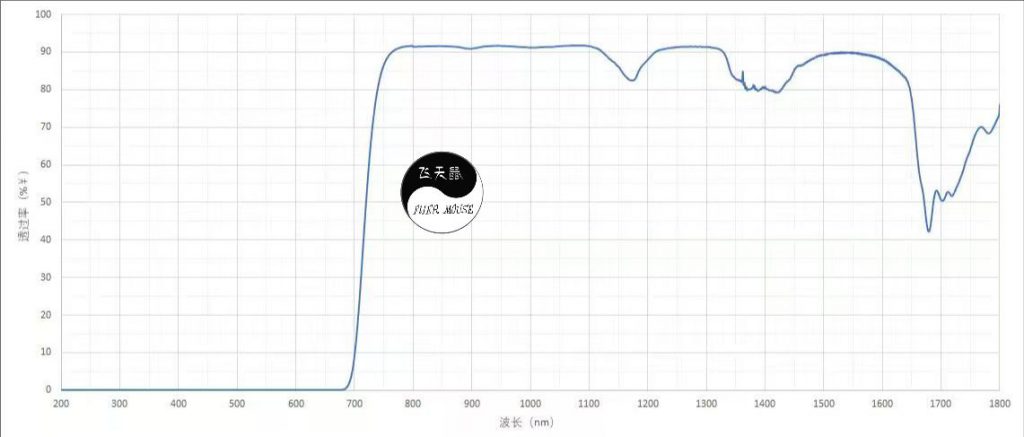
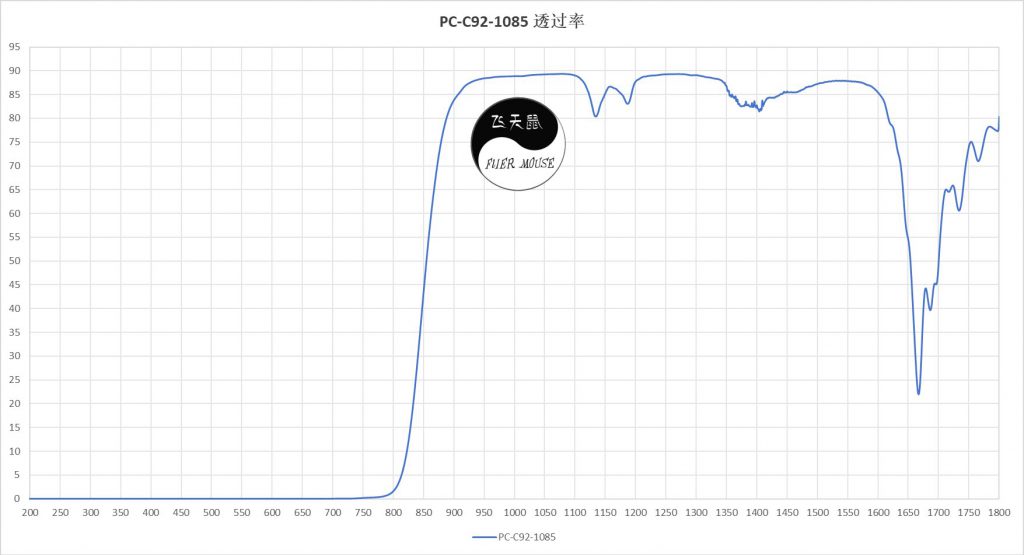
- Optical Performance: Designed for efficient light transmission in the 650–1650 nm NIR range (black appearance), compatible with various IR LED wavelengths.
- Enhanced Weather Resistance: Overcomes UV degradation limitations of standard PC, significantly improving anti-aging performance.
- Retained PC Advantages: High heat resistance (137°C), impact strength, flame retardancy, and mechanical durability.
- R&D & Specifications
- Selective Light Transmission: The FLIERMOUSE NIR PC C92 Series modifies PC polymer side chains or additive formulations to block visible light while enabling high NIR transmission (black appearance) without compromising base PC properties.
- Customizable Wavelengths: Supports sub-bands within 650–1650 nm (e.g., 650~1650 nm, 700~1650 nm, 780~1650 nm, 850~1650 nm, 905~1650 nm, 940~1650 nm), adapting to diverse IR LED wavelengths in sensors/cameras.
- Technical Classification: Categorized by transmission peaks (e.g., 850 nm, 940 nm, 1550 nm) and cutoff bands for precise application matching.
III. Key Application Fields (Focused on NIR Transmissive PC)
- Autonomous Driving & Automotive
- ADAS Systems: LiDAR windows, in-car camera lenses—requiring high IR transmission, heat resistance, and impact strength.
- Lighting & Sensing: Headlamp covers, IR night vision components—ensuring optical stability in harsh environments.
- Electronics & Security
- Surveillance: IR camera filters, smart lock sensor windows—enabling covert IR illumination.
- Consumer Electronics: Navigation modules for robotic vacuums, smart home sensor housings.
- Optics & Medical
- Optical Lenses: IR lenses, medical endoscopes—balancing transmittance and sterilization resistance.
- Medical Devices: Surgical tool casings, sterilization containers—leveraging chemical resistance and biocompatibility.
- Aerospace & Defense
- Instrument Protection: Aircraft IR detection windows, astronaut visors—demanding extreme-environment reliability.
- Military Equipment: Night vision goggles, IR scopes—adapted to complex battlefield conditions.
IV. NIR Transmissive PC vs. Standard PC: Key Differences
| Property | Standard PC | NIR Transmissive PC |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Band | Visible light (380–700 nm) | NIR (650–1650 nm) |
| UV Resistance | Poor (prone to yellowing) | Excellent (UV-modified) |
| Appearance | Transparent/translucent | Black (IR-transmissive, opaque to visible light) |
| Typical Uses | Structural parts, lenses | IR sensing, LiDAR, surveillance |
V. Market Outlook & Challenges
- Growth Drivers
- Rising demand for IR sensors in smart vehicles, robotics, and 5G IoT—global LiDAR market projected to exceed $10 billion by 2030.
- Upgraded needs for high-precision optical materials in medical and security fields.
- Technical Challenges
- Balancing transmittance and mechanical properties during modification.
- Cost-performance optimization vs. optical glass (e.g., scaling production).
VI. Conclusion

FLIERMOUSE’s NIR transmissive PC (NIR PC C92 Series) enables selective wavelength transmission and enhanced durability, positioning it as a critical material for smart sensing. Its engineered modifications make it indispensable in automotive ADAS, robotic navigation, medical devices, optical systems, and surveillance. As IR technology proliferates, the FLIERMOUSE NIR PC C92 Series will expand applications, driving the shift from “transparent optics” to “intelligent IR perception” and leading the next-gen engineering plastics revolution.NIR-transmissive thermoplastic(PC-C92-1073) with high transmittance (92%)at 850nm/940nm.
Home
Services
Services
发表回复